Alignment: Journey to Student Learning
“Assessments should reveal how well students have learned what we want them to learn while instruction ensures that they learn it. For this to occur, assessments, learning objectives, and instructional strategies need to be closely aligned so that they reinforce one another” Carnegie Mellon University Eberly Center Teaching Excellence & Educational Innovation.
What is Alignment?
Alignment is when assessments measure whether students have achieved learning objectives, and when instructional materials, learning activities, and tools help prepare students for the assessments.
The relationship between learning objective and assessment is like a journey for the student, being on a path or climbing a mountain, in that the learning materials students reference, the activities they do, and the tools students utilize, support the student reaching the goal of successfully achieving the objective as measured by the assessment.
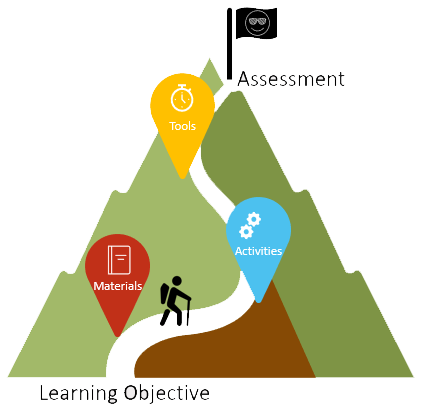
We start by considering a learning objective, and then devise a way to assess whether that learning objective is achieved. But, before that, there’s the teaching in which we incorporate instructional materials, have students complete activities, and utilize tools that all work together to help students prepare for the assessment.
Alignment Example
Consider the following example of alignment. The learning objective is that the student can evaluate sources based on the CRAAP (currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose) criteria. The assessment is designed so that students evaluate sources to determine reputability based on the CRAAP criteria. Because the assessment is designed to measure achievement of the learning objective, the learning objective and assessment are aligned. Providing students with reputable and non-reputable websites, and having students locate reputable websites while using the “CRAAP Test” tool to explain the criteria, allows students to practice and prepare for success on the assessment.
Learning Objective
6. The student will ethically evaluate sources, including digital content, by:
b. determining the currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose of sources.
Materials
Websites (reputable and non-reputable)
Activities
Locate reputable websites and explain how each meets the standards of currency, relevancy, authority, accuracy, and purpose.
Tools
“CRAAP Test” template document
Assessment
For the website provided, explain whether it is reputable based upon its currency, relevancy, authority, accuracy, and purpose.
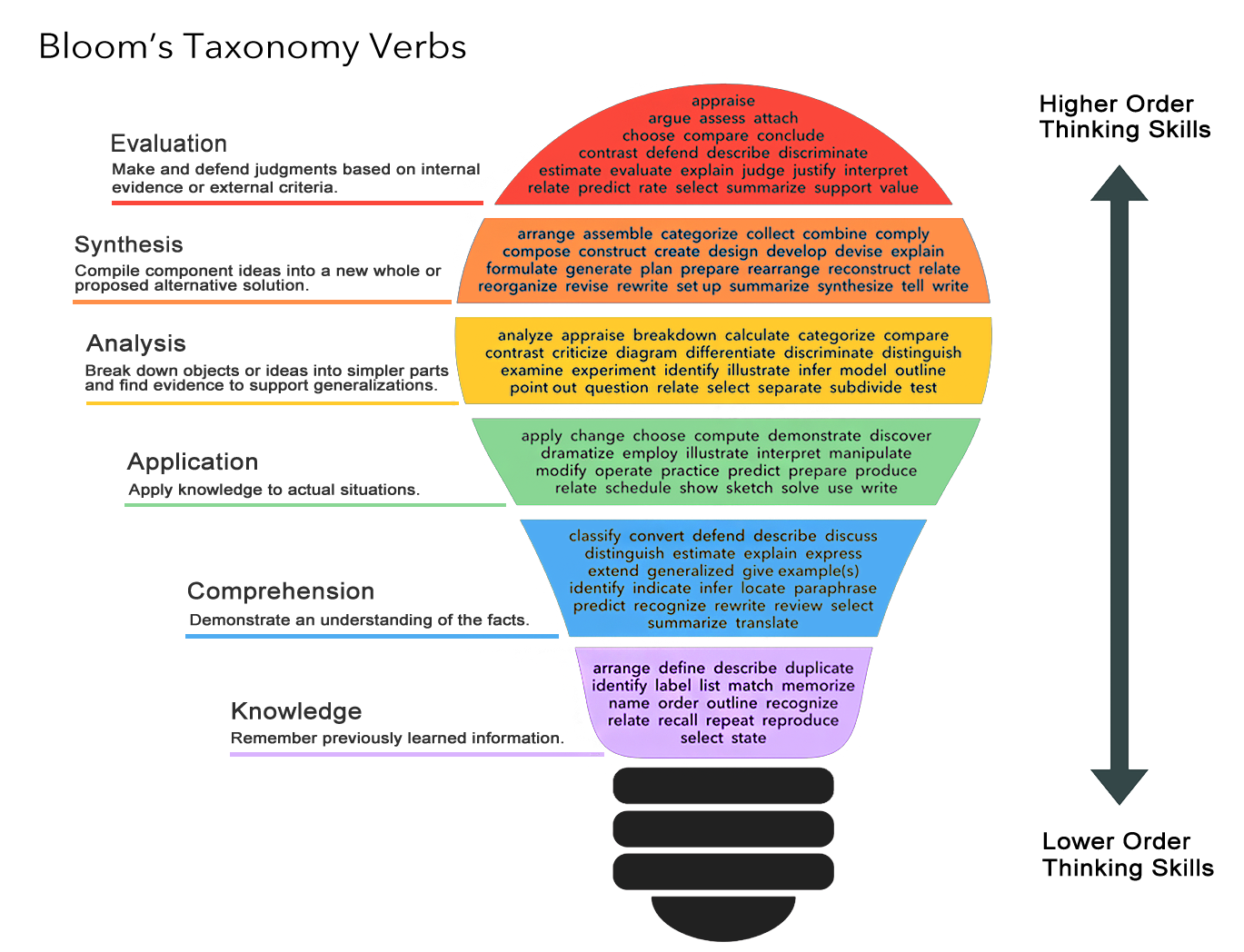
Levels of Thinking – Bloom’s Taxonomy
Along with aligning learning objectives to assessments, another aspect to consider is the expected level of thinking skills. As illustrated by Bloom’s Taxonomy, the levels are somewhat hierarchical, and we would want to help students step through these in order, not expecting them to jump into higher order thinking before they’ve demonstrated lower level thinking.
Why is Alignment Important?
Aligning assessments to learning objectives helps assure that students meet the intended goals of a course. What are these goals? They are the Learning Outcomes and Objectives as described in every Approved Course Outline at St. Petersburg College (SPC). Alignment validates these course outcomes, which in turn ensures SPC, the State of Florida, and grant standards are being met. This guarantees students are being taught what they’re supposed to be taught. For a student, this ensures that when they transfer, they can be assured that their prerequisites or degree from SPC will support them wherever they go. This works in reverse, too. When SPC receives students from other colleges we’re trusting that those courses are aligned as well, because alignment provides a cohesion between institutions.
Evaluating Alignment in Your Course
- Use the IDEAS Alignment Worksheet to:
- Identify an assessment from your course.
- List the learning objective(s) that the assessment measures.
- Identify the Bloom’s verb and level.
- Evaluate the current effectiveness of the alignment and make a plan of action.
- List the activities, materials, and tools that teach the concepts the objective(s) cover.
- Use the ACUE Assessment Alignment by Cognitive Levels document to consider examples of the types of assessment based upon the type and cognitive level of learning outcome.
Note: If you are teaching a standard or master course, contact the course coordinator to suggest updates.
Resources
- Webinar Presentation (PowerPoint Download)
- Webinar Recording (46:43)
- Why should assessments, learning objectives, and instructional strategies be aligned?
- Alignment in Assessment
- The Hidden Power of Alignment in Quality Matters Standards
- Mapping the Journey of Alignment
- Website Evaluation
- Bloom’s Taxonomy Verbs
- Bloom’s Taxonomy (updated)
- Bloom’s Taxonomy Wheel
- Faculty Voice: Alignment – Stephanie Watkins (1:29)
- CurricUNET
- CurrIQunet META (coming soon)
- Demo: Getting Started with Alignment (1:39)
- IDEAS Alignment Worksheet
- ACUE Assessment Alignment by Cognitive Levels
Feedback? IDEAS Event Feedback Form
Questions? IDEAS@SPCollege.edu




